Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Konovalov, S. V.; Mikhailovskii, A. B.*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Takizuka, Tomonori; Shirokov, M. S.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 47(12B), p.B223 - B236, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.62(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Neoclassical Tearing Modes, NTMs, are known to limit the maximum attainable plasma pressure, degrade confinement and, at worst, culminate in disruption of the tokamak discharges. Key role in NTM evolution belongs to the radial profiles of the plasma flow, temperature and density which are determined by the conjunction of the longitudinal and cross-filed transport arising from thermal conduction, particle diffusion, and viscosity. In this report the influence of anomalous perpendicular heat transport and anomalous ion perpendicular viscosity on early stage of the NTM evolution is studied theoretically.
Suzuki, Takahiro; Isayama, Akihiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Fujita, Takaaki; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Sakata, Shinya; Sueoka, Michiharu; Hosoyama, Hiroki*; Seki, Masami; JT-60 Team
AIP Conference Proceedings 787, p.279 - 286, 2005/09
A real-time control system of safety factor (q) profile was developed in JT-60. This system, for the first time, enables 1) real time evaluation of q profile using local magnetic pitch angle measurement by motional Stark effect (MSE) diagnostic and 2) control of current drive (CD) location (rhoCD) by adjusting the parallel refractive index 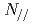 of lower-hybrid (LH) waves through the change of phase difference (dphi) of LH waves between multi-junction launcher modules. The method for q profile evaluation was newly developed, without time-consuming reconstruction of equilibrium, so that the method requires less computational time. The system evaluates q profile within every 10ms, which is much faster than current relaxation time, typically order of 1s. Safety factor profile by the real-time calculation agreed well with that by equilibrium reconstruction with MSE. From temporal evolution of q (or current) profile, we evaluate CD location in real-time, too. The control system controls rhoCD through
of lower-hybrid (LH) waves through the change of phase difference (dphi) of LH waves between multi-junction launcher modules. The method for q profile evaluation was newly developed, without time-consuming reconstruction of equilibrium, so that the method requires less computational time. The system evaluates q profile within every 10ms, which is much faster than current relaxation time, typically order of 1s. Safety factor profile by the real-time calculation agreed well with that by equilibrium reconstruction with MSE. From temporal evolution of q (or current) profile, we evaluate CD location in real-time, too. The control system controls rhoCD through 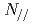 (or directly dphi) in such a way to minimize difference between the real-time evaluated q profile and its reference profile. The real-time control system was applied to positive shear plasmas (
(or directly dphi) in such a way to minimize difference between the real-time evaluated q profile and its reference profile. The real-time control system was applied to positive shear plasmas (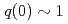 ), having plasma current of 0.6MA, toroidal field of 2.3T, and electron density of
), having plasma current of 0.6MA, toroidal field of 2.3T, and electron density of 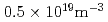 . In order to keep good coupling of LH waves to the plasma, gap between the launcher and the plasma surface was controlled to about 0.1m. The reference q profile was set to q(0)=1.3. The real-time q profile approached to the reference after application of real-time control; the controlled q profile was sustained for 3s, which was limited by injected LH power. RF experiments in JT-60U, such as stabilization of neo-classical tearing modes, plasma startup experiments, etc., are also presented.
. In order to keep good coupling of LH waves to the plasma, gap between the launcher and the plasma surface was controlled to about 0.1m. The reference q profile was set to q(0)=1.3. The real-time q profile approached to the reference after application of real-time control; the controlled q profile was sustained for 3s, which was limited by injected LH power. RF experiments in JT-60U, such as stabilization of neo-classical tearing modes, plasma startup experiments, etc., are also presented.
Konovalov, S. V.; Mikhailovskii, A.*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Takizuka, Tomonori; Shirokov, M. S.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko
Proceedings of 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2004) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/11
Influence of anomalous perpendicular heat transport and anomalous perpendicular viscosity on conditions of Neoclassical Tearing Mode onset is studied theoretically. Series of different parallel transport mechanisms competitive to anomalous cross-island heat conductivity in the perturbed temperature profile are considered.In the transport threshold model, magnetic curvature effect is as much important as bootstrap drive weakened by the finite perpendicular heat transport. Perpendicular viscosity brings island-rotation-frequency dependence of the transport threshold model.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; Ozeki, Takahisa
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 80(7), p.605 - 613, 2004/07
Neoclassical tearing mode stabilization by an electron cyclotron wave current drive (ECCD) has been studied by using the numerical model on the basis on the modified Rutherford eq. coupled with the 1.5D transport code and the EC code. Numerical model almost reproduces the JT-60U experimental results. Undetermined parameters in the modified Rutherford equation are estimated from JT-60U experiments. Sensitivity of stabilization to the EC current location is investigated. Low EC current and peaked EC current profile mitigates the sensitivity, while higher EC current and the peaked EC current profile moves the rational surface more largely through the background current modification by ECCD and intensify the sensitivity. High EC current and broad EC current profile also mitigates the sensitivity. EC current necessary for the full stabilization is studied. The necessary EC current much depends on the parameters of bootstrap current and ECCD terms in the modified Rutherford equation. Necessary ECCD power on ITER is evaluated on the basis of parameters estimated from JT-60U experiments.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Ozeki, Takahisa; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Takizuka, Tomonori
Nuclear Fusion, 44(4), p.477 - 487, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:72.74(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)NTM stabilization by ECCD has been numerically studied in order to evaluate the necessary EC power for the stabilization of NTM on ITER. The time evolution of an island width of NTM is calculated by the modified Rutherford equation. The modification of background current profile by the EC current is calculated by the current diffusion equation and the variation of the tearing stability index  ' is taken into account. When the EC power is higher than a threshold value, NTM with any island width can be fully stabilized. The dependence of the threshold power on parameters in the modified Rutherford equation is examined. The threshold power much depends on the parameters of the bootstrap current term in the modified Rutherford equation. The injected EC current decreases the value of
' is taken into account. When the EC power is higher than a threshold value, NTM with any island width can be fully stabilized. The dependence of the threshold power on parameters in the modified Rutherford equation is examined. The threshold power much depends on the parameters of the bootstrap current term in the modified Rutherford equation. The injected EC current decreases the value of  ' through the background current modification, which results in the reduction of the threshold power. The effects of the peakedness of EC current profile and the EC power modulation on the threshold power are investigated. When the width of the EC current profile becomes half, the threshold power is reduced to half or less. The EC power modulation is inessential for the threshold power reduction if the EC current profile can be peaked. Considering the maximum value of the threshold power in the range of the parameters, the EC power of about 25 MW is found to be sufficient for the simultaneous stabilization of both the
' through the background current modification, which results in the reduction of the threshold power. The effects of the peakedness of EC current profile and the EC power modulation on the threshold power are investigated. When the width of the EC current profile becomes half, the threshold power is reduced to half or less. The EC power modulation is inessential for the threshold power reduction if the EC current profile can be peaked. Considering the maximum value of the threshold power in the range of the parameters, the EC power of about 25 MW is found to be sufficient for the simultaneous stabilization of both the 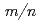 =3/2 and 2/1 mode NTM on ITER.
=3/2 and 2/1 mode NTM on ITER.
Mukhovatov, V.*; Shimada, Michiya; Chudnovskiy, A. N.*; Costley, A. E.*; Gribov, Y.*; Federici, G.*; Kardaun, O. J. F.*; Kukushkin, A. S.*; Polevoi, A. R.*; Pustovitov, V. D.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 45(12), p.235 - 252, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:82.78(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)ITER will be the first magnetic confinement device with burning DT plasma and fusion power of about 0.5 GW. During the past few years, new results have been obtained that substantiate the confidence in achieving Q  10 in ITER with inductive H-mode operation. These include achievement of a good H-mode confinement near the Greenwald density at high triangularity of the plasma cross section; improvements in theory-based confinement projections for the core plasma; improvement in helium ash removal due to the elastic collisions of He atoms with D/T ions in the divertor predicted by modelling; demonstration of feedback control of NTMs and resultant improvement in the achievable beta-values; better understanding of ELM physics and development of ELM mitigation techniques; and demonstration of mitigation of plasma disruptions. ITER will have a flexibility to operate also in steady state and intermediate (hybrid) regimes. The paper concentrates on inductively driven plasma performance and discusses requirements for steady-state operation in ITER.
10 in ITER with inductive H-mode operation. These include achievement of a good H-mode confinement near the Greenwald density at high triangularity of the plasma cross section; improvements in theory-based confinement projections for the core plasma; improvement in helium ash removal due to the elastic collisions of He atoms with D/T ions in the divertor predicted by modelling; demonstration of feedback control of NTMs and resultant improvement in the achievable beta-values; better understanding of ELM physics and development of ELM mitigation techniques; and demonstration of mitigation of plasma disruptions. ITER will have a flexibility to operate also in steady state and intermediate (hybrid) regimes. The paper concentrates on inductively driven plasma performance and discusses requirements for steady-state operation in ITER.
Takizuka, Tomonori
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 79(11), p.1123 - 1129, 2003/11
no abstracts in English
Mikhailovskii, A. B.*; Shirokov, M. S.*; Tsypin, V. S.*; Konovalov, S. V.; Ozeki, Takahisa; Takizuka, Tomonori; Galv o, R. M. 0.*; Nascimento, I. C.*
o, R. M. 0.*; Nascimento, I. C.*
Physics of Plasmas, 10(10), p.3975 - 3983, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:25.85(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A transport threshold model of subsonic neoclassical tearing modes (NTMs) in tokamaks is developed. The basic procedure is to include the velocity-dependent term into the single-fluid heat-conductivity equation. and to supply the parallel plasma motion equation. These equations permit the determination of the perturbed plasma temperature and the bootstrap current drive of NTMs, for both strong and weak perpendicular heat transport. It is shown that the subsonic NTMs transport threshold model can be more realistic than the standard transport threshold model of NTMs.
Mikhailovskii, A. B.*; Shirokov, M. S.*; Tsypin, V. S.*; Konovalov, S. V.*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Takizuka, Tomonori; Galv o, R. M. 0.*; Nascimento, I. C.*
o, R. M. 0.*; Nascimento, I. C.*
Physics of Plasmas, 10(9), p.3790 - 3792, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:16.93(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A fluid treatment of convective-transport threshold model of neoclassical tearing modes (NTMs) in tokamaks is developed. A system of moment equations of the drift kinetic equation with a model perpendicular transport is derived. The essence of this moment equation system is to allow for the parallel heat flux on an equal footing with pressure and temperature. The suggested moment equation system is applied for analyzing the bootstrap current drive of NTMs. As a result, a threshold model of these modes is derived, which coincides qualitatively with the convective-transport threshold model initially formulated by means of intuitive consideration.
Mikhailovskii, A. B.*; Churikov, A. P.*; Konovalov, S. V.; Shirokov, M. S.*; Tsypin, V. S.*
Doklady Physics, 48(4), p.159 - 162, 2003/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.86(Mechanics)It is shown that there is a new class of perturbations, limiting the pressure of ideally stable plasma in the conditions of fusion reactors of tokamak type. localization of such modes includes three characteristic regions: large-scale (MHD), Larmor and sub-Larmor ones. It is suggested that these modes can be responsible for spontaneous generation of neoclassical tearing modes observed experimentally.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Ozeki, Takahisa; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Takizuka, Tomonori
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.5, p.519 - 522, 2002/00
Stabilizing simulation of the neoclassical tearing mode by an electron cyclotron current drive (ECCD) in JT-60 superconducting tokamak has been done by using a 1.5D time-dependent tokamak code TOPICS and the modified Rutherford's equation. A local EC current in the center of the island stabilizes the mode. However, the EC current off the center moves the rational surface and decreases the stabilizing effect of EC. Necessary range of EC current location for the stabilization becomes wider for low EC power, or narrower for high EC power, when the EC current profile is more peaked. The long duration of EC injection widens this range. Peaked EC current profile, early injection and long injection duration lower the minimum EC power necessary for the stabilization.
Ozeki, Takahisa; Isayama, Akihiko
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 77(5), p.409 - 419, 2001/05
Neoclassical tearing modes (NTMs) which are induced by lack of the bootstrap current inside the magnetic island are reviewed based on the modified Rutherford equation. Theoretical bases and experimental observations of NTM are described. The beta value scaling of the growth of NTM and the mechanism of the growth are discussed. Influence of NTM on energy confinement is described, and the stabilization of NTM by electron cyclotron current drive (ECCD) is introduced.
Ozeki, Takahisa; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Isayama, Akihiko; Kurita, Genichi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 53(1-4), p.65 - 69, 2001/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:48.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
ITER Physics Expert Group on Disruptions, Plasma Control, and MHD
Nuclear Fusion, 39(12), p.2251 - 2389, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Hirayama, Toshio; Sugie, Tatsuo; Sakasai, Akira; Yoshino, Ryuji;
JAERI-M 91-169, 15 Pages, 1991/10
no abstracts in English
Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Azumi, Masafumi
Kaku Yugo Kenkyu, 65(SPECIAL ISSUE), p.225 - 241, 1991/03
no abstracts in English
Tokuda, Shinji; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Tsunematsu, Toshihide; Takeda, Tatsuoki
Int. Conf. on Plasma Physics, p.925 - 928, 1989/00
no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 6965, 24 Pages, 1977/02
no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 5934, 15 Pages, 1974/12
no abstracts in English
Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
Comparisons between flux driven full-f gyrokinetic simulations and gradient driven delta-f gyrokinetic simulations are discussed with respect to i) turbulent momentum transport and ii) plasma size and power scaling of ion temperature gradient driven turbulence. In the former problem, the ambipolar condition including both turbulent and neoclassical transport is essential in estimating momentum transport and resulting plasma rotation profiles. In the latter problem, self-consistent interactions between temperature fluctuations and turbulent transport under a local power balance condition lead to the power degradation of confinement. These mechanisms are unique to full-f simulations and give significant impact on the estimation of plasma confinement performances.